Nanobots to be deployed in fight against Cancer
By Stella Law
 医疗纳米机器人的出现让人们不再惧怕癌症
医疗纳米机器人的出现让人们不再惧怕癌症
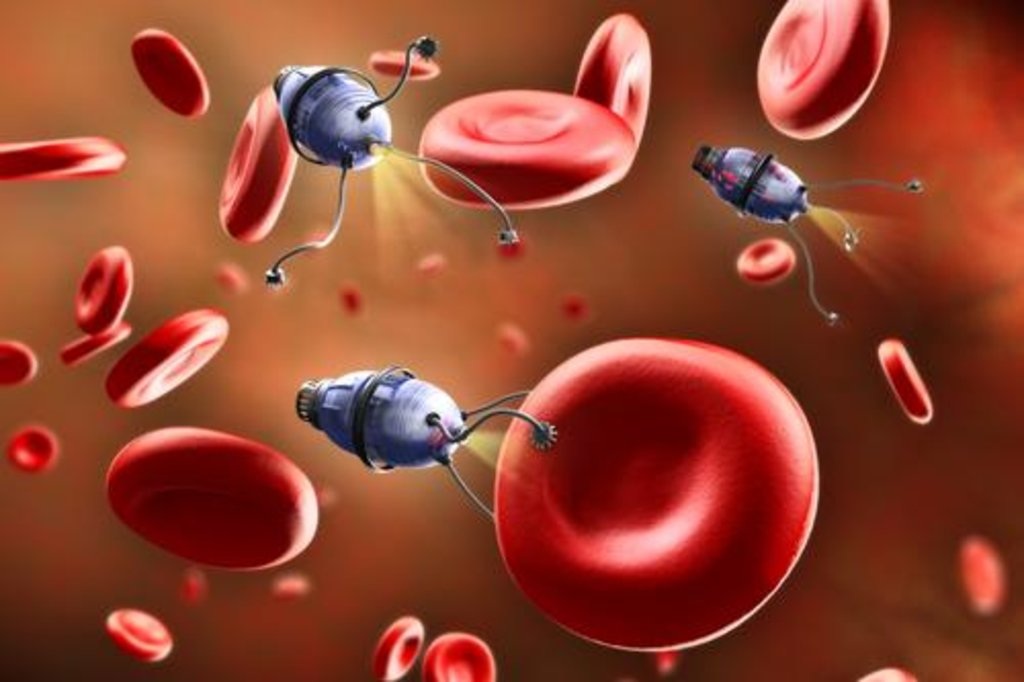
自 DNA 纳米机器人诞生以来,科学家们一直对这种新技术充满期待,特别是在治疗癌症上。想象一下,如果患者患有肿瘤,这种微小的DNA机器人能够“潜入”患者体内并完成定位,最后操作一个“小型手术”,将会有多少生命能被挽救回来。
中国科学院国家纳米科学与技术中心(NCNST)赵宇亮和丁宝全两位博士领导的研究团队与美国亚利桑那州立大学(ASU)生物设计研究所分子设计和仿生学中心主任颜灏博士的实验室合作,对这种纳米机器人及其工作原理进行了详细描述。
研究人员称,通过选择性地切断血液供应来“饿死”肿瘤的效果是很引人注目的。例如,如果阻断血液,几个小时就能够从肿瘤的状态看到效果,并且适用于几乎任何类型的肿瘤。
While it definitely sounds bizarre and indistinguishable from a sci-fi movie plot, the day is probably not too far when tiny robots, known as nanobots, will roam freely inside your body to detect and cure various health hazards, including humanity’s worst nemesis: Cancer.
What is Nanotechnology?
The genesis of organized attempts to blend nanoscience and technology goes way back to the late 1950s. The movement was spearheaded by renowned physicist, Richard Feynman, who, in 1959, outlined a process to manipulate and control individual atoms and molecules.

Richard Feyman
Nanotechnology has made quite a splash in virtually all major disciplines of science and technology, with scientists and engineers finding methods to create material at the nano scale for various usages, including in the healthcare sector.
A nanobot is typically a tiny device of 0.1-10 micrometres (a micrometre is one-millionth of a metre) in size. Being the size of a red blood cell or even smaller, it can’t carry traditional robotic elements, such as motors and chips.
Instead, these bioengineered bots are made of DNA strands and they’re capable of administering small doses of drugs with great precision.
Nanobots and Cancer Treatment
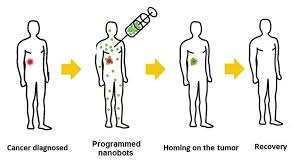
In a major nanomedicine breakthrough in February 2018, researchers discovered a new prospect for the treatment of cancer using nanobots.
A joint study by scientists from Arizona State University and the National Centre for Nanoscience and Technology (NCNST) found that nanobots can be successfully programmed to treat cancerous tumours by cutting off their blood supply.
The study was published in the journal Nature, and based on its finding, we can safely say that the initial tests were, by and large, successful in shrinking cancerous tumours in mice.
 Here’s how it Works
Here’s how it Works
In order to test the nanobot’s capability, scientists made use of a mouse tumour model infected with human cancer cells to induce aggressive growth in the tumour. Thereafter, nanobots, with a blood clotting enzyme called thrombin attached to its surface, were deployed to counter the growth of the tumour.
For those out of the loop, thrombin is an enzyme that blocks blood flow to the tumour-associated blood vessels, thereby hampering its growth and eventually eliminating it.
 But, how do we determine that the nanobots would target only the cancer cells and won’t harm the surrounding healthy cells, as usually happens in traditional cancer treatments, like chemotherapy and radiation?
But, how do we determine that the nanobots would target only the cancer cells and won’t harm the surrounding healthy cells, as usually happens in traditional cancer treatments, like chemotherapy and radiation?
The answer lies in the programming of the nanobot. For optimal result, the nanobot must carry a specially designed payload called the DNA aptamer.
The DNA aptamer, once activated, can target a special protein called the nucleolin, which is usually found in high amounts on the surface of cancerous cells.
These pre-programmed nanobots work in a congregation to surround the tumour just hours after injection and administer the thrombin enzyme into the heart of the tumour.
The Challenge
While it all sounds relatively easy in theory, the real challenge is to ensure that the nanobots can reach the exact location where the cancer cells are growing. On top of that, the bots have to stay there unharmed for enough time to get the job done successfully. This can be one heck of a challenge, if we take the speed and frequency of blood flow into account.
 Tracing the nanobots accurately once they are injected could be another big challenge, since they are too small to show up on an X-ray and any other conventional imaging techniques. Tracking is non-optional to ensure that the nanobots are doing their intended work.
Tracing the nanobots accurately once they are injected could be another big challenge, since they are too small to show up on an X-ray and any other conventional imaging techniques. Tracking is non-optional to ensure that the nanobots are doing their intended work.
Additionally, the doctors also might have to remove any adversely affected tissue during the treatment procedure, which wouldn’t be easy if they are unable to pinpoint the location of nanobots.
At the current juncture, nanotechnology is a technology that is full of hype, cynicism, and of course, loads of promises. If we are able to harness its true power using the right combination of technologies, then it might not be too far when cancer will stop being a leading cause of death worldwide.